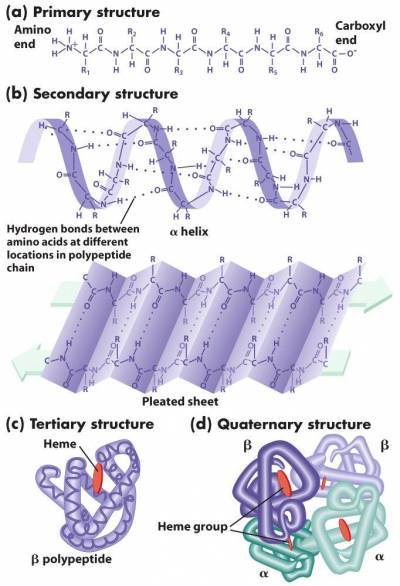
Protein structures can be classified into four main categories. Primary, secondary, tertiary and quanternary. Primary protein structure is the amino acid sequence. Secondary protein structure is the amino acid sequence folded into alpha helices and beta sheets. Tertiary protein structure are those alpha helices and beta sheets folded into protein subunits. And quanternary protein structure is a combination of folded protein tertiary structures. An example of a quanternary protein structure would be hemoglobin because it contains four subunits.
Quanternary and protein structures can be denatured and transformed to primary protein structures by heat. For example an egg that is in its raw state can be said to be tertiary protein structure but when its fried on a frying pan the tertiary protein structure linearizes to primary protein structure. Note that the fried egg in its primary protein structure can no longer be transformed into tertiary structure. However in labs it is possible to transform primary protein structures(amino acid sequences) into folded proteins(teritary or quanternary proteins) by using bacteria or yeast systems. But we will discuss this a later time.
|