Gram positive bacteria cell walls retain a crystal violet when stained with the gram stain. They have a thick peptidoglycan layer which helps them retain this stain. Gram positive bacteria walls also have teichoic acids which are polyanionic polymers of either ribitol phosphate or glycerol phosphate joined by phosphodiester bonds. They make up betweeen 30 to 60 percent of the dry weight of the wall.
Gram Negative cell walls consist of LPS or lipopolysaccharide which has a lipid A core and a repeating oligosacharide which can be called somatic antigen. Bacteria that do not have the oligosacharide have less virulence. LPS is an endotoxin that increases the pathogenicity of the bacteria. LPS is usally released when the bacteria is lysed. Gram negative bacteria also have a thin peptidoglycan layer.
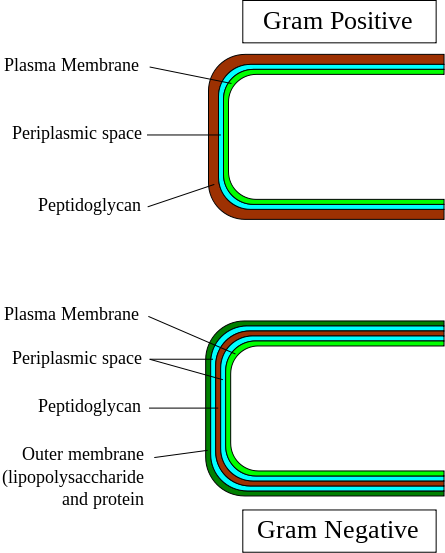
Source:The Physiology and Biochemistry of Prokaryotes by David White 4th edition
|